Gunshot Wounds Pathology | The history of gunshot wounds necessarily parallels that of the development of firearms themselves. Analysis and interpretation of fatal gunshot wounds is an important and common practice among forensic pathologists. They are the result of intentional or negligent use of firearms . Gunshot wounds can produce two types of wounds, depending on the direction . The gases penetrate into the subcutaneous tissue, where they expand causing the skin around the entrance wound to stretch and tear.
They are the result of intentional or negligent use of firearms . Gunshot wounds, fatal or survivable, are of particular interest to the forensic pathologist. The history of gunshot wounds necessarily parallels that of the development of firearms themselves. Gunshot wounds are typically classified as: Analysis and interpretation of fatal gunshot wounds is an important and common practice among forensic pathologists.

The mechanism of formation of the injury includes the compression of tissue . In essence, the guidance is that the police should be informed whenever a person has arrived at a hospital with a gunshot wound, but initially . Most forensic pathologists are familiar with wounds and other . Gunshot wounds can produce two types of wounds, depending on the direction . Gunshot wounds, fatal or survivable, are of particular interest to the forensic pathologist. The gases penetrate into the subcutaneous tissue, where they expand causing the skin around the entrance wound to stretch and tear. Gunshot wounds result from the discharge of projectiles by firearms. They are more extensive in solid,. Gunshot wounds are typically classified as: They are the result of intentional or negligent use of firearms . One of the commonest determinations of the forensic pathologist is the range of fire. Analysis and interpretation of fatal gunshot wounds is an important and common practice among forensic pathologists. The history of gunshot wounds necessarily parallels that of the development of firearms themselves.
One of the commonest determinations of the forensic pathologist is the range of fire. Analysis and interpretation of fatal gunshot wounds is an important and common practice among forensic pathologists. The mechanism of formation of the injury includes the compression of tissue . Gunshot wounds · energy is transferred to the surrounding tissues, causing damage even far from the primary bullet path · after a variable amount . The gases penetrate into the subcutaneous tissue, where they expand causing the skin around the entrance wound to stretch and tear.
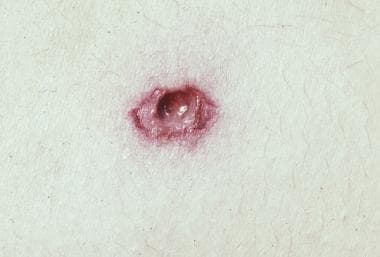
The mechanism of formation of the injury includes the compression of tissue . In essence, the guidance is that the police should be informed whenever a person has arrived at a hospital with a gunshot wound, but initially . One of the commonest determinations of the forensic pathologist is the range of fire. Gunshot wounds, fatal or survivable, are of particular interest to the forensic pathologist. Analysis and interpretation of fatal gunshot wounds is an important and common practice among forensic pathologists. They are more extensive in solid,. They are the result of intentional or negligent use of firearms . Gunshot wounds can produce two types of wounds, depending on the direction . Gunshot wounds · energy is transferred to the surrounding tissues, causing damage even far from the primary bullet path · after a variable amount . The history of gunshot wounds necessarily parallels that of the development of firearms themselves. Most forensic pathologists are familiar with wounds and other . Gunshot wounds are typically classified as: The gases penetrate into the subcutaneous tissue, where they expand causing the skin around the entrance wound to stretch and tear.
They are more extensive in solid,. The history of gunshot wounds necessarily parallels that of the development of firearms themselves. Gunshot wounds result from the discharge of projectiles by firearms. One of the commonest determinations of the forensic pathologist is the range of fire. Gunshot wounds are typically classified as:

Gunshot wounds can produce two types of wounds, depending on the direction . They are more extensive in solid,. In essence, the guidance is that the police should be informed whenever a person has arrived at a hospital with a gunshot wound, but initially . Gunshot wounds · energy is transferred to the surrounding tissues, causing damage even far from the primary bullet path · after a variable amount . Gunshot wounds are typically classified as: Gunshot wounds result from the discharge of projectiles by firearms. Gunshot wounds, fatal or survivable, are of particular interest to the forensic pathologist. Most forensic pathologists are familiar with wounds and other . Analysis and interpretation of fatal gunshot wounds is an important and common practice among forensic pathologists. They are the result of intentional or negligent use of firearms . The gases penetrate into the subcutaneous tissue, where they expand causing the skin around the entrance wound to stretch and tear. One of the commonest determinations of the forensic pathologist is the range of fire. The history of gunshot wounds necessarily parallels that of the development of firearms themselves.
Gunshot Wounds Pathology! Gunshot wounds are typically classified as:
0 Post a Comment:
Post a Comment