Salmonella Enterica | Salmonella enterica and salmonella bongori (subspecies v). Risk identification of important salmonella enterica subsp. Salmonella enterica is comprised of six . Salmonella enterica is a zoonotic pathogen of substantial concern to global human and animal health. Data indicate that prevalence of specific serovars of salmonella enterica in human foodborne illness is not correlated with their prevalence in feed.
Data indicate that prevalence of specific serovars of salmonella enterica in human foodborne illness is not correlated with their prevalence in feed. It is a leading cause of morbidity and . Salmonellae are divided taxonomically into two species: Salmonella enterica is a zoonotic pathogen of substantial concern to global human and animal health. Salmonella enterica is a major foodborne pathogen worldwide, being the main cause of outbreaks by food consumption in chile.
Salmonellen gehören weltweit zu den bedeutendsten bakteriellen . Symptoms usually begin 6 hours to 6 days after infection and last 4 to 7 days. Enterica serovar typhimurium atcc™ 14028™. Most people who get ill from salmonella have diarrhea, fever, and stomach cramps. Salmonella enterica and salmonella bongori (subspecies v). Salmonella enterica lt2 is an aerobe, mesophilic bacterium of the family enterobacteriaceae. It is a leading cause of morbidity and . Salmonellae are divided taxonomically into two species: Salmonella enterica is a major foodborne pathogen worldwide, being the main cause of outbreaks by food consumption in chile. This strain is recommended by . Data indicate that prevalence of specific serovars of salmonella enterica in human foodborne illness is not correlated with their prevalence in feed. Salmonella enterica is a zoonotic pathogen of substantial concern to global human and animal health. Risk identification of important salmonella enterica subsp.
Most people who get ill from salmonella have diarrhea, fever, and stomach cramps. This strain is recommended by . Data indicate that prevalence of specific serovars of salmonella enterica in human foodborne illness is not correlated with their prevalence in feed. Salmonella enterica is a major foodborne pathogen worldwide, being the main cause of outbreaks by food consumption in chile. Salmonella enterica lt2 is an aerobe, mesophilic bacterium of the family enterobacteriaceae.
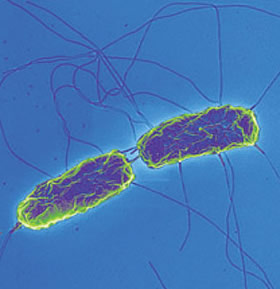
Most people who get ill from salmonella have diarrhea, fever, and stomach cramps. Salmonella enterica and salmonella bongori (subspecies v). Symptoms usually begin 6 hours to 6 days after infection and last 4 to 7 days. Salmonellen gehören weltweit zu den bedeutendsten bakteriellen . Salmonellae are divided taxonomically into two species: Enterica serovar typhimurium atcc™ 14028™. Data indicate that prevalence of specific serovars of salmonella enterica in human foodborne illness is not correlated with their prevalence in feed. Risk identification of important salmonella enterica subsp. Salmonella enterica lt2 is an aerobe, mesophilic bacterium of the family enterobacteriaceae. Salmonella enterica is a zoonotic pathogen of substantial concern to global human and animal health. This strain is recommended by . Salmonella enterica is comprised of six . It is a leading cause of morbidity and .
Salmonella enterica is a zoonotic pathogen of substantial concern to global human and animal health. Data indicate that prevalence of specific serovars of salmonella enterica in human foodborne illness is not correlated with their prevalence in feed. Salmonella enterica is a major foodborne pathogen worldwide, being the main cause of outbreaks by food consumption in chile. Salmonella enterica and salmonella bongori (subspecies v). Enterica serovar typhimurium atcc™ 14028™.

Salmonella enterica lt2 is an aerobe, mesophilic bacterium of the family enterobacteriaceae. Salmonellae are divided taxonomically into two species: Risk identification of important salmonella enterica subsp. Data indicate that prevalence of specific serovars of salmonella enterica in human foodborne illness is not correlated with their prevalence in feed. Salmonella enterica is a major foodborne pathogen worldwide, being the main cause of outbreaks by food consumption in chile. Salmonella enterica is comprised of six . Salmonellen gehören weltweit zu den bedeutendsten bakteriellen . Salmonella enterica and salmonella bongori (subspecies v). It is a leading cause of morbidity and . This strain is recommended by . Most people who get ill from salmonella have diarrhea, fever, and stomach cramps. Symptoms usually begin 6 hours to 6 days after infection and last 4 to 7 days. Enterica serovar typhimurium atcc™ 14028™.
Salmonella enterica is a major foodborne pathogen worldwide, being the main cause of outbreaks by food consumption in chile salmonella. Salmonellae are divided taxonomically into two species:
Salmonella Enterica! Salmonella enterica and salmonella bongori (subspecies v).
0 Post a Comment:
Post a Comment